Welcome to Linyi Kemele Co., Ltd
Important Nitrates

Important nitrates properties and uses
· Background and Overview
Nitrate is a salt of nitric acid, an ionic compound, generally in the form of crystals. Almost all metal nitrates are soluble in water and are relatively stable at room temperature. Solid nitrates will decompose at high temperatures and become oxidative, and will burn or even explode when encountering organic matter. The properties of metal cations are different, and the situation of thermal decomposition is also different. The most active metal, that is, the metal (mainly alkali metals and alkaline earth metals) with a potential sequence before magnesium, nitrate decomposes into nitrite and oxygen; the potential sequence is between magnesium and copper. The metal nitrate in the middle decomposes into the corresponding metal oxide, nitrogen dioxide and oxygen; the metal nitrate in the potential sequence after copper decomposes to produce the corresponding elemental substance, nitrogen dioxide and oxygen. In fact, the decomposition of nitrate goes through the process of nitrite and oxide, but the stability of nitrite and oxide of various metals is different, so some decompose into metal oxide, and some decompose into metal element, some The only thing that can be nitrite is the common point of these three situations, that is, oxygen occurs. Nitrate is an oxidant at high temperature, and it is used to make fireworks and black powder based on this property. Black powder is a mixture of potassium nitrate (68%), sulfur (15%) and carbon (17%), which was invented in my country in the 7th century. However, the aqueous solution of nitrate has almost no oxidizing property, and nitrate can be identified by the "brown ring test" method. The corresponding nitrate can be obtained by dissolving metal in nitric acid or reacting metal oxide with nitric acid. Nitrogen contained in nitrate is easily absorbed by plants and is an important nitrogen fertilizer, such as sodium nitrate and calcium nitrate. Potassium nitrate and ammonium nitrate can both It can be used as fertilizer and explosives.
· Properties and uses of important nitrates
Potassium nitrate: KNO3, colorless or white crystal, soluble in water, insoluble in absolute ethanol. The specific gravity is 2.1, the melting point is 336°C, and the decomposition temperature is 400°C. When mixed with organic matter and combustible matter, it is easy to catch fire and explode when heated, rubbed, and impacted. Sacks soaked in potassium nitrate will spontaneously ignite. It is a primary inorganic oxidizing agent. Used as black powder, fireworks, medicine, analytical reagent, oxidant, etc.
Sodium nitrate: NaNO3, white translucent crystal, slightly deliquescent, soluble in water and alcohol. The specific gravity is 2.26, the melting point is 308°C, and the decomposition temperature is 380°C. It can be decomposed by heating to release oxygen, and it can explode when the reaction is violent. When mixed with organic matter and combustibles, heating or ignition can cause strong combustion. It is a primary inorganic oxidizing agent. Used in the manufacture of dyes, glass, enamel, medicine, etc.
Ammonium nitrate: NH4NO3, white crystal, deliquescent, soluble in water and ethanol. The specific gravity is 1.73, the melting point is 169.6°C, and the decomposition temperature is 210°C. It can explode when mixed with organic matter and combustibles by heating, impact, and friction. There is also a danger of explosion by itself by rapid heating (300°C) or impact. It is a primary organic oxidant used in the manufacture of explosives, fertilizers, reagents, etc.
Lead nitrate: Pb(NO3)2, white crystal, soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol. The specific gravity is 4.53, the melting point is 470°C, and it decomposes at the melting point. Toxic, mixed with organic matter, reducing agent and combustibles such as sulfur and phosphorus, it may cause combustion or explosion hazard after slight friction. Paper impregnated with alkaline lead nitrate can ignite spontaneously after drying. It is a secondary inorganic oxidizing agent. Used as a mordant, fireworks, and the manufacture of lead salts.
Mercury nitrate: Hg(NO3)2, colorless or white transparent crystal, deliquescent, easily soluble in water. The specific gravity is 4.39, the melting point is 79°C, and the decomposition temperature is 180°C. When heated, it decomposes and releases toxic vapors. Mixed with organic matter, reducing agent, combustible sulfur, phosphorus, etc., there is a danger of burning or explosion. It is a secondary inorganic oxidizing agent, used in organic synthesis, manufacture of medicines and mercury.
· Preparation
There are many kinds of nitrates, taking the preparation of potassium nitrate as an example:
Method 1: Potassium chloride reacts in 65% nitric acid at 75°C to generate potassium nitrate, chlorine gas, and nitrosyl chloride. When nitrosyl chloride is oxidized with nitric acid, chlorine gas and nitrogen dioxide escape, and the latter is oxidized with air and absorbed by water to recover nitric acid.
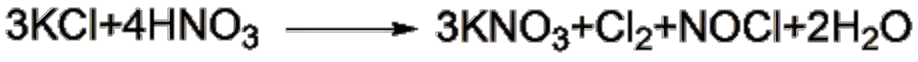
Method 2: Solvent extraction method At 5-10°C, dissolve potassium chloride in nitric acid with a concentration of 60%-70%, extract with an organic solvent, and separate potassium nitrate and hydrochloric acid.
Method 3: Neutralization method Use potassium hydroxide or potassium carbonate to neutralize nitric acid, and obtain potassium nitrate through evaporation and crystallization; or use potassium hydroxide or potassium carbonate solution to absorb the tail gas in the production of nitric acid and process it to obtain potassium nitrate.
· Main reference
[1] Encyclopedia of Chinese Middle School Teaching Chemistry Volume
[2] Chinese Fire Protection Dictionary
[3] Encyclopedia of China (Volume of Chemical Industry)
The news information released by the platform is only provided as knowledge, and is only for reference and communication of industry insiders, and does not guarantee its accuracy and completeness. You should not use this as a substitute for your own independent judgment, so any information should be at your own risk and has nothing to do with Kemele. If there is any infringement, please contact us to delete!
Next: 2023 China Chemical Industry Expo